The triptans are 5-HT1D/1B receptor agonists that inhibit release of vasoactive neuropeptides. Serotonin (5HT) is a key mediator in the pathogenesis of migraine.

Consistent with the 5HT hypothesis of migraine, 5HT receptor agonists are a mainstay for acute treatment of migraine headaches.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
The triptans interact potently with 5HT1B and 5HT1D receptors and have a low or no affinity for other subtypes of 5HT receptors or for α1 and α2 adrenergic, β adrenergic, dopaminergic, muscarinic cholinergic, and benzodiazepine receptors.
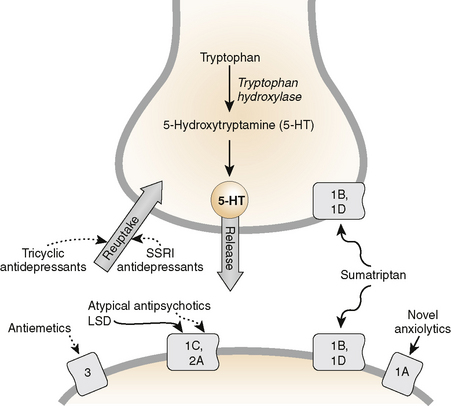
Two primary hypotheses have been proposed to explain the actions of these drugs.
First, the triptans, the ergot alkaloids, and antidepressants may activate 5-HT1D/1B receptors on presynaptic trigeminal nerve endings to inhibit the release of vasodilating peptides, and antiseizure agents may suppress excessive firing of these nerve endings.
Second, the vasoconstrictor actions of direct 5-HT agonists (the triptans and ergot) may prevent vasodilation and stretching of the pain endings. It is possible that both mechanisms contribute in the case of some drugs.
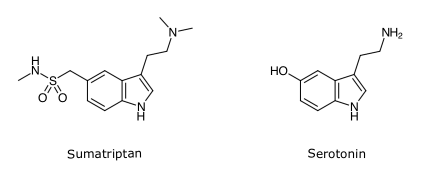
Sumatriptan and the other triptans are selective agonists for 5-HT1D and 5-HT1B receptors.
These receptor types are found in cerebral and meningeal vessels and mediate vasoconstriction. They are also found on neurons and probably function as presynaptic inhibitory receptors.
The triptans are indole derivatives. Their capacity to decrease the nausea and vomiting of migraine is an important advance in the treatment of the condition.
Available compounds include almotriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan.
ADVERSE EFFECTS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
Triptans may cause nausea and vomiting. They should probably be avoided in women who are pregnant, and in patients with hemiplegic or basilar migraine, a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), or uncontrolled hypertension. In patients whose hypertension is controlled, triptans are commonly used safely, although caution is advised.
The most common side effect of sumatriptan nasal spray is a bitter taste. Triptans can cause paresthesias; asthenia and fatigue; flushing; feelings of pressure, tightness, or pain in the chest, neck, and jaw; drowsiness; dizziness; nausea; and sweating.
In the extreme, these agents can cause serotonin syndrome, a consequence of a generalized excess of 5HT at 5HT receptors, especially when used in combination with SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and MAO inhibitors.
![serotonin_syndrome [TUSOM | Pharmwiki]](/tmedweb_tulane_edu/pharmwiki/lib/exe/fetch_php/serotoninrx.png)
The triptans are contraindicated in patients with a history of ischemic or vasospastic coronary artery disease (including history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks), cerebrovascular or peripheral vascular disease, hemiplegic or basilar migraines, other significant cardiovascular diseases, or ischemic bowel diseases.
Tricyclic antidepressants
TCA amitriptyline has shown efficacy for migraine prevention.